The Dental Specialty of Oral Pathology in Canada
Oral pathology and oral medicine is a recognized specialty of dentistry in Canada. The word “pathology” refers to the diagnosis of medical conditions. Oral pathology deals with the nature, identification, and treatment of oral diseases and conditions.
Oral Pathologists
Oral pathologists in Canada are trained in specialized dental programs and certified as dental specialists. They focus more on the soft tissues of the mouth than the teeth.
Some of the most common diseases and conditions oral pathologists may look for include:
- Oral cancers
- The herpes simplex virus
- Fungal infections
- TMD
- Ulcers
- Periodontal diseases
- Tongue enlargement
- Jaw misalignment
- Cleft palate or cleft lip
Pathology and Oral Medicine
Oral medicine and oral pathology are a single dental specialty in Canada, but each requires different types of training. While oral pathology is mostly directed at the diagnosis of oral diseases and conditions, oral medicine is more focused on the treatment of these issues, especially in cases of medically complex patients.
Learn More About Oral Medicine
Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
Oral and maxillofacial pathology is a separate specialty from oral medicine and oral pathology. Oral and maxillofacial pathology is often broader, looking at oral diseases and conditions as well as those that affect the surrounding hard and soft tissues of the mouth and face. This includes the salivary glands, TMJ, and orofacial skin, as well as head and neck pathology.
Learn More About Oral and Maxillofacial Pathology
Tools & Techniques in Oral Pathology
Dental pathologists use a variety of tools, techniques, and technology to understand, diagnose, and treat abnormalities in the mouth. These include examination techniques, testing techniques, and biopsies.
Examinations
Typically, the first step an oral pathologist will take to diagnose an issue in the mouth is a complete oral examination.
Some of the symptoms or abnormalities that may be discovered in an examination include:
- Growths, lumps, or swellings
- Ulcers
- Cysts
- Abscesses
- Lesions
- Infections
- Salivary gland disorders
- TMJ issues
- Facial pain
- Taste and smell disorders
- Unerupted teeth
- Mucosal abnormalities
Examinations will also look at a variety of risk factors that may be present, including genetic predispositions to certain conditions, lifestyle factors such as tobacco and alcohol consumption, and other health or medical issues that may be causing abnormalities in the mouth.
Testing
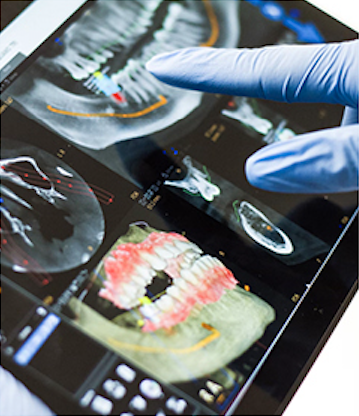
Testing and diagnostic tools for oral medicine may include imaging techniques such as ultrasounds, MRIs (magnetic resonance imaging), PETs (positron emission tomography), CTs (computed tomography), and x-rays. Blood tests may also be requested.
Oral pathologists often work closely with other medical professionals, including oral radiologists, to locate and assess abnormalities that can’t be seen in a typical examination. They may also be called upon by general dentists to read data from imaging tools in complex situations.
Biopsies
Tissue biopsies are diagnostic tests in which a small sample of affected tissue is taken from the site of the abnormality. The tissue is then sent to a laboratory for testing. Biopsies are most often used when there is a risk or indication of oral cancer.
Find a Dental Specialist
You can search the 123Dentist network of dental specialists to find an oral medical practitioner or oral pathologist in Canada. If you have experienced abnormalities in your mouth or you’re concerned about your oral health, be sure to see a dentist or dental specialist for diagnosis and treatment.