Oral Cancer Screening
Some things are easy to miss if you’re not looking for them.
Oral cancer doesn’t always come with pain. Sometimes it’s just a patch that doesn’t go away. A sore that feels slow to heal. A spot you keep biting accidentally. You might not think much of it—but your dentist will.
That’s what a screening is for. It’s not invasive. It doesn’t take long. But it could catch something early, when it’s easier to treat. Because waiting until it hurts? That’s waiting too long.
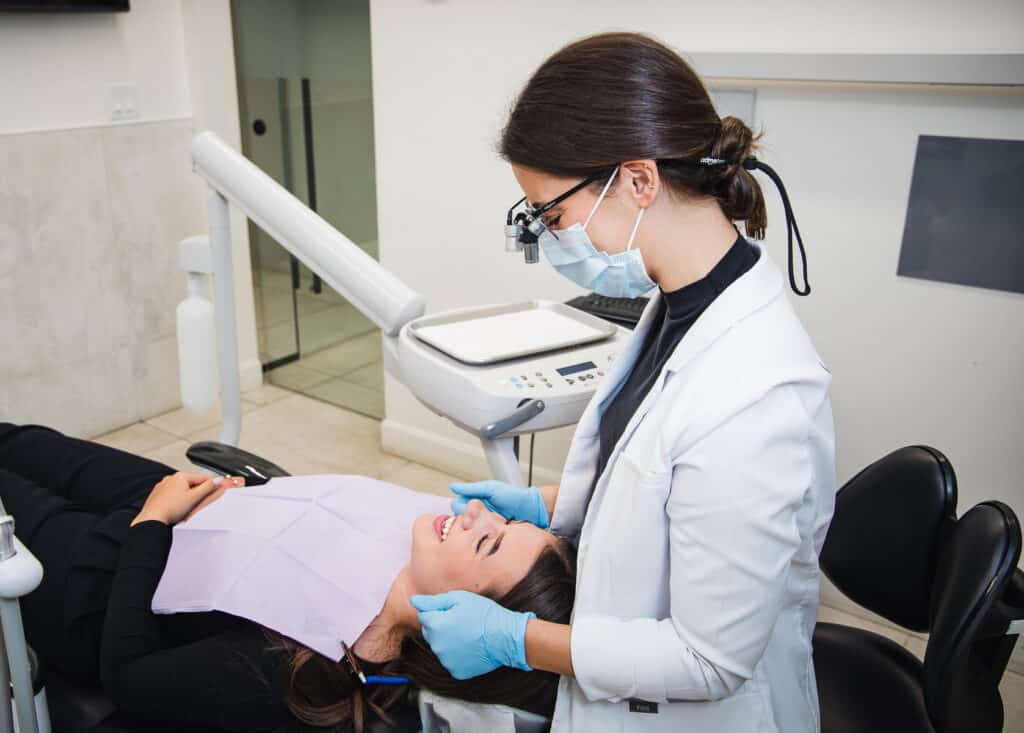
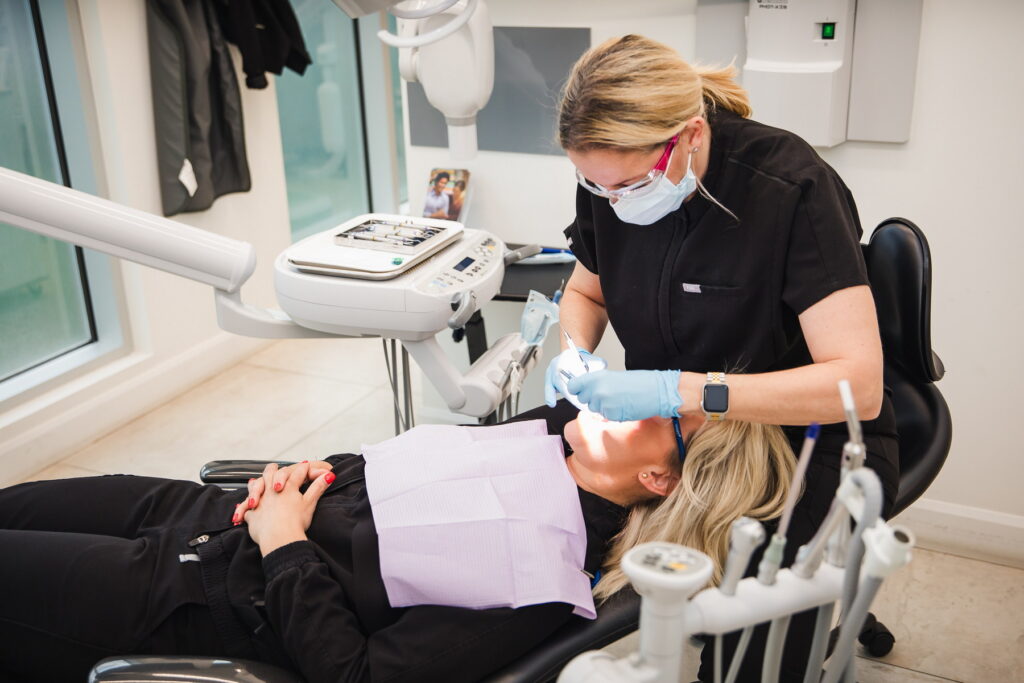
Early detection matters more than perfect prevention.
You can do everything right—brush, floss, avoid tobacco—and still develop signs of concern. Screening doesn’t assume something’s wrong. It just gives your provider a chance to check.
Oral cancer screening is part of many regular dental visits. It involves a visual and physical exam of the soft tissues in your mouth: tongue, cheeks, roof, floor, gums, lips, throat. Your dentist may feel around your neck and jawline, too.
They’re looking for:
• Unusual patches (white, red, or mixed)
• Lumps or swelling
• Areas that bleed or crust over
• Changes in texture or movement
• Soreness that doesn’t seem to resolve
It’s quick. It’s gentle. And it could make all the difference.
The screening is done in your chair. No sedation. No downtime. Just a few minutes of focused attention from someone trained to notice what you might not.
What happens:
• Your dentist asks a few questions—about symptoms, family history, past issues
• They examine your mouth, tongue, and throat
• They may gently press on the sides of your neck or under your jaw
• If anything looks unusual, they’ll explain next steps—often a photo or referral
You might walk away with reassurance. You might walk away with a plan. Either way, you’re not left wondering.

Your Oral Cancer Screening questions, answered.
Yes. While smoking raises your risk, oral cancer can affect anyone—including people with no known risk factors.
If they see something unusual, they’ll talk to you about it clearly and calmly. Sometimes it’s nothing. Sometimes they recommend a closer look from a specialist.
Often, yes. Many dentists include a basic screening during routine visits, especially for adults over 40.
You’ll likely need more frequent monitoring. Your dentist can coordinate with your care team to make sure nothing slips through the cracks.
It depends on your provider. Some plans include screening under preventive care. Ask your clinic team if you’re not sure—they’ll help check.
Catching something early starts with looking.
Oral cancer screening is one of the simplest things you can do to protect your long-term health. If it’s been a while—or if something feels off—book a visit. Your mouth has a lot to say, even when it’s quiet.